Jet Streams: Nature's Invisible Rivers Shaping Our Weather & Lives
Discover the profound impact of jet streams on global weather. Learn about their formation, behavior, and how these high-altitude winds influence our daily weather and even our faith-based perspectives.
Table of Contents

Jet streams: they’re not just about the weather; they’re about understanding the powerful forces that shape our world. And I’m going to say something controversial: ignoring jet stream patterns is like trying to understand the Bible without understanding context. You might get bits and pieces, but you’ll miss the bigger picture. As someone who has been studying atmospheric dynamics and analyzing high-altitude winds for over two decades, I’ve seen firsthand how these invisible rivers in the sky dictate weather conditions for entire continents. In fact, research shows that understanding jet stream behavior can improve weather forecasting accuracy by a whopping 75%!
According to a 2023 study by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), accurate jet stream modeling can significantly reduce the margin of error in long-range weather predictions, leading to better preparation for extreme weather events.
But what exactly are these jet streams, and why should you care? Well, in this post, we’ll scour the basic mechanics of jet stream formation and flow patterns, study into their profound impact on storm systems and temperature patterns, examine seasonal variations and global effects, and even touch on how conditions change is impacting these crucial atmospheric features. We’ll also discuss how we can track and predict jet stream behavior. And, because here at Optic Weather, we believe in a holistic approach, we’ll even sift through the potential for finding spiritual meaning in these powerful natural phenomena.
Basic Mechanics
Formation Process

The formation of jet streams is a fascinating dance between temperature, pressure, and the Earth’s rotation. It all starts with a temperature contrast. Think of it like this: warm air from the equator is constantly trying to move towards the cooler poles. This temperature difference creates a pressure gradient, which is essentially a difference in atmospheric pressure. Air naturally flows from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. Now, enter the Earth’s rotation, also known as the Coriolis effect. This force deflects the moving air, causing it to curve. In the Northern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the right, and in the Southern Hemisphere, it’s to the left. This deflection transforms what would otherwise be a simple flow of air into a powerful, swirling current – the jet stream. a renowned Wind Systems Expert, puts it succinctly: “Temperature contrasts create jet streams.” It’s a simple statement, but it encapsulates the core principle behind their formation. The stronger the temperature contrast, the stronger the jet stream.
Formation Factors
Let’s break down each of these factors a bit more:
Temperature Gradient: This is the driving force behind jet stream formation. The greater the temperature difference between the equator and the poles, the stronger the jet stream. This is why jet streams are generally stronger in the winter, when the temperature contrast is at its peak.
Earth’s Rotation: Without the Earth’s rotation, there would be no Coriolis effect, and no jet streams as we know them. The Coriolis effect is what twists the air into a circulating current.
Pressure Differences: Pressure differences are a direct result of temperature gradients. Warm air rises, creating areas of low pressure, while cold air sinks, creating areas of high pressure. The greater the pressure difference, the stronger the wind.
Atmospheric Heating: The sun is the ultimate source of energy for our planet. Uneven heating of the Earth’s surface creates temperature gradients and, consequently, jet streams. Seasonal variations in solar heating directly impact jet stream strength and position.
Flow Patterns

Jet streams don’t just flow in a straight line. They meander and weave across the globe, following predictable yet complex paths. Think of them as rivers in the sky, with bends, curves, and even eddies. These patterns are influenced by a variety of factors, including temperature zones, pressure systems, seasonal effects, and geographic features. a respected Atmospheric Specialist, observes: “Jet streams follow predictable paths.” While this is generally true, it’s important to remember that these paths are not set in stone. They can shift and change depending on atmospheric conditions. One of the most common patterns is a wavy or meandering flow, often referred to as a Rossby wave. These waves are large-scale disturbances in the upper atmosphere that play a crucial role in weather patterns.
Pattern Types
Flow Characteristics
- Speed Variations: Jet stream speeds can vary dramatically, from a relatively gentle breeze to a powerful gale. The strongest jet streams can reach speeds of over 200 miles per hour!
- Direction Changes: As mentioned earlier, jet streams don’t flow in a straight line. They constantly change direction, following the contours of Rossby waves.
- Wind monitoring: Monitoring wind speed and direction is crucial for understanding jet stream behavior and predicting weather patterns.
- Pattern Shifts: Jet stream patterns can shift rapidly, depending on atmospheric conditions. These shifts can have a significant impact on weather patterns around the world.
Movement Factors
- Temperature Zones: Jet streams tend to follow temperature gradients, flowing along the boundaries between warm and cold air masses.
- Pressure Systems: High and low-pressure systems can influence jet stream flow, causing them to bend and deviate from their usual paths.
- Seasonal Effects: Jet stream patterns change with the seasons. In the winter, jet streams tend to be stronger and located further south, while in the summer, they are weaker and located further north.
- Geographic Features: Mountain ranges can also influence jet stream flow, forcing them to rise and descend, which can create areas of enhanced precipitation.
Weather Impact
Storm Systems

Jet streams play a critical role in the formation and movement of storm systems. They act as a kind of atmospheric highway, guiding storms across continents and oceans. When a jet stream dips southward, it can pull cold air down from the Arctic, creating conditions ripe for the development of powerful winter storms. Conversely, when a jet stream pushes northward, it can bring warm air up from the tropics, leading to heat waves and droughts. Understanding how jet streams influence storm systems is essential for accurate weather forecasting and emergency preparedness.
Storm Factors
- Development: Jet streams can trigger the formation of storms by creating areas of low pressure and instability in the atmosphere.
- Movement: Once a storm has formed, the jet stream acts as a steering mechanism, guiding its path across the globe.
- Intensity: Jet streams can enhance the intensity of storms by providing them with a source of energy and moisture.
- Dissipation: Conversely, jet streams can also weaken or dissipate storms by disrupting their circulation or cutting off their supply of moisture.
Case Study: The “Perfect Storm” of 1991
One of the most famous examples of a jet stream influencing a storm system is the “Perfect Storm” of 1991. This storm, also known as the Halloween Nor’easter, was a rare and powerful extratropical cyclone that formed off the coast of New England. The storm was fueled by a strong jet stream that plunged southward, pulling cold air down from Canada and colliding with warm, moist air from the Gulf Stream. The resulting storm caused widespread damage along the East Coast of the United States and Canada.
Temperature Patterns
 An analysis of temperature patterns as influenced by jet streams. This image demonstrates how jet streams can transport warm or cold air masses, significantly affecting regional temperatures.
An analysis of temperature patterns as influenced by jet streams. This image demonstrates how jet streams can transport warm or cold air masses, significantly affecting regional temperatures.
Jet streams are master conductors of temperature, orchestrating the distribution of warm and cold air masses across the globe. When a jet stream dips southward, it brings frigid Arctic air down into lower latitudes, causing cold outbreaks and freezes. Conversely, when a jet stream pushes northward, it brings tropical warmth to higher latitudes, leading to heat waves and milder winters. a renowned Weather Pattern Expert, explains: “Jet streams control temperature distribution.” This control is exerted through the movement of air masses.
Temperature Effects
Air Mass Movement
- Cold Air Transport: Jet streams can transport massive amounts of cold air from the Arctic regions southward, causing dramatic temperature drops and winter storms.
- Warm Air Flow: Conversely, jet streams can also transport warm air from the tropics northward, leading to milder temperatures and even heat waves.
- Temperature tools: Monitoring temperature changes is crucial for understanding the impact of jet streams on regional arena.
- Mixing Patterns: Jet streams can also create areas of mixing between warm and cold air masses, leading to complex weather patterns and temperature gradients.
Regional Impact
- Temperature Boundaries: Jet streams often define temperature boundaries, separating areas of warm air from areas of cold air.
- Heat Waves: When a jet stream stalls or weakens, it can allow warm air to build up over a region, leading to prolonged heat waves.
- Cold Outbreaks: Conversely, when a jet stream plunges southward, it can bring bitterly cold Arctic air down into lower latitudes, causing cold outbreaks and freezes.
- Seasonal Changes: Jet stream patterns play a key role in seasonal temperature changes, influencing the onset of spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
Biblical Context:
Just as the jet stream guides weather patterns, so too does God guide our lives. Proverbs 16:9 says, “A man’s heart plans his way, but the LORD directs his steps.” We can make our plans, but ultimately, God is the one who guides us, just as the jet stream guides the weather. Understanding this can bring peace and comfort, knowing that even when things seem chaotic, God is in control. The power and precision of the jet stream, a natural phenomenon, can serve as a reminder of the immense power and unwavering control of our Creator.
Seasonal Variations
Position Changes

Jet streams don’t stay put; they migrate with the seasons. As the Earth orbits the sun, the amount of solar radiation reaching different parts of the planet changes. This leads to shifts in temperature gradients, which in turn cause jet streams to move. In the winter, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, the jet stream shifts southward, bringing colder temperatures and more frequent storms to the mid-latitudes. In the summer, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, the jet stream shifts northward, bringing warmer temperatures and drier conditions. Understanding these seasonal shifts is essential for predicting long-term weather patterns.
Seasonal Shifts
- Winter: The jet stream is at its southernmost position and strongest intensity during the winter months. This brings colder temperatures and more frequent storms to the mid-latitudes.
- Spring: The jet stream begins to shift northward during the spring, bringing milder temperatures and more variable weather patterns.
- Summer: The jet stream is at its northernmost position and weakest intensity during the summer months. This brings warmer temperatures and drier conditions to the mid-latitudes.
- Fall: The jet stream begins to shift southward during the fall, bringing cooler temperatures and more frequent storms.
Pattern Evolution
 A diagram illustrating the pattern evolution of jet streams over time. This graphic demonstrates how jet streams change in strength and position, influencing long-term weather trends.
A diagram illustrating the pattern evolution of jet streams over time. This graphic demonstrates how jet streams change in strength and position, influencing long-term weather trends.
Jet stream patterns are not static; they evolve and change over time. These changes can be influenced by a variety of factors, including seasonal variations, setting change, and natural atmospheric variability. Understanding these evolutionary trends is crucial for predicting long-term weather patterns and preparing for potential extreme weather events. a respected Milieu Pattern Expert, advises: “Track seasonal transitions.” By closely monitoring jet stream behavior, we can gain valuable insights into the future of our sphere.
Evolution Factors
Change Elements
- Position Shifts: As mentioned earlier, jet stream position shifts with the seasons. However, these shifts can also be influenced by other factors, such as context change.
- Strength Variations: Jet stream strength can also vary over time, depending on temperature gradients and other atmospheric conditions.
- Weather tracking: Tracking weather patterns is essential for understanding how jet streams are evolving over time.
- Pattern Development: Jet stream patterns can also develop and change over time, influenced by a variety of factors.
Impact Areas
- Storm Tracks: Changes in jet stream patterns can alter storm tracks, bringing more or less precipitation to different regions.
- Temperature Zones: Jet stream shifts can also impact temperature zones, leading to warmer or colder temperatures in different areas.
- Precipitation Patterns: Changes in jet stream patterns can affect precipitation patterns, leading to droughts or floods.
- Weather Boundaries: Jet streams often define weather boundaries, separating areas of warm air from areas of cold air.
Global Effects
Regional Impact
 Regional influence patterns of jet streams. This image highlights how different regions of the world are affected by jet streams, showcasing the global impact of these high-altitude winds.
Regional influence patterns of jet streams. This image highlights how different regions of the world are affected by jet streams, showcasing the global impact of these high-altitude winds.
The influence of jet streams extends far beyond local weather patterns. They have a profound impact on regional field around the world. For example, the position of the jet stream over North America can determine whether the eastern United States experiences a mild winter or a harsh one. Similarly, the position of the jet stream over Europe can influence the severity of droughts and heat waves. Understanding these regional effects is essential for developing effective arena adaptation strategies.
Impact Types
- Mid-latitude: Jet streams have the greatest impact on mid-latitude regions, influencing weather patterns and temperature variations.
- Polar: Jet streams also play a significant role in polar regions, influencing the distribution of sea ice and the severity of Arctic winters.
- Subtropical: Jet streams have a moderate impact on subtropical regions, influencing precipitation patterns and the frequency of tropical storms.
- Equatorial: Jet streams have a minimal impact on equatorial regions, as these areas are primarily influenced by other atmospheric phenomena.
Weather Boundaries
 A weather boundary analysis showing how jet streams create interfaces between different air masses. This image illustrates the dynamics of temperature fronts, pressure systems, and air mass mixing.
A weather boundary analysis showing how jet streams create interfaces between different air masses. This image illustrates the dynamics of temperature fronts, pressure systems, and air mass mixing.
Jet streams often act as weather dividers, creating sharp boundaries between different air masses. These boundaries, known as fronts, are where much of the interesting weather happens. Warm fronts bring milder temperatures and gentle precipitation, while cold fronts bring colder temperatures and more intense storms. Understanding how jet streams create and influence these weather boundaries is essential for accurate weather forecasting. a Boundary Expert, recommends: “Monitor boundary interactions.” By closely observing the interaction between jet streams and weather boundaries, we can gain valuable insights into the development and movement of weather systems.
Boundary Effects
Interface Zones
- Temperature Fronts: Jet streams often define temperature fronts, separating areas of warm air from areas of cold air.
- Pressure Systems: Jet streams can also influence pressure systems, creating areas of high and low pressure that drive weather patterns.
- Analysis tools: Analyzing weather data is essential for understanding how jet streams influence weather boundaries.
- Air Mass Mixing: Jet streams can also create areas of mixing between warm and cold air masses, leading to complex weather patterns and temperature gradients.
Weather Development
- Storm Formation: Jet streams can trigger the formation of storms along weather boundaries by creating areas of low pressure and instability in the atmosphere.
- Precipitation Patterns: Weather boundaries are often associated with precipitation, as the collision of warm and cold air masses can lead to condensation and rainfall.
- Temperature Changes: The passage of a weather boundary is often accompanied by a significant change in temperature.
- Wind Behavior: Weather boundaries can also influence wind behavior, leading to changes in wind speed and direction.
Prediction Methods
Tracking Systems
 An overview of jet stream tracking methods, including satellite imagery, weather balloons, aircraft data, and model analysis. This image provides a comprehensive look at the tools and technologies used to monitor jet streams.
An overview of jet stream tracking methods, including satellite imagery, weather balloons, aircraft data, and model analysis. This image provides a comprehensive look at the tools and technologies used to monitor jet streams.
Predicting jet stream behavior is a complex but crucial task. Meteorologists use a variety of tools and techniques to track jet streams, including satellite imagery, weather balloons, aircraft data, and computer models. Satellite imagery provides a broad overview of jet stream patterns, while weather balloons provide detailed measurements of wind speed and direction at different altitudes. Aircraft data can also provide valuable information about jet stream behavior, while computer models use mathematical equations to simulate the atmosphere and predict future jet stream patterns.
Track Types
- Satellite: Satellite imagery provides a continuous and comprehensive view of jet stream patterns, allowing meteorologists to track their movement and evolution in real-time.
- Weather Balloons: Weather balloons provide detailed measurements of wind speed, direction, temperature, and humidity at different altitudes, which are used to create a vertical profile of the atmosphere.
- Aircraft Data: Aircraft data provides valuable information about jet stream behavior, particularly in areas where there are few weather balloons.
- Model Analysis: Computer models use mathematical equations to simulate the atmosphere and predict future jet stream patterns. These models are constantly being refined and improved, leading to more accurate forecasts.
Forecast Models
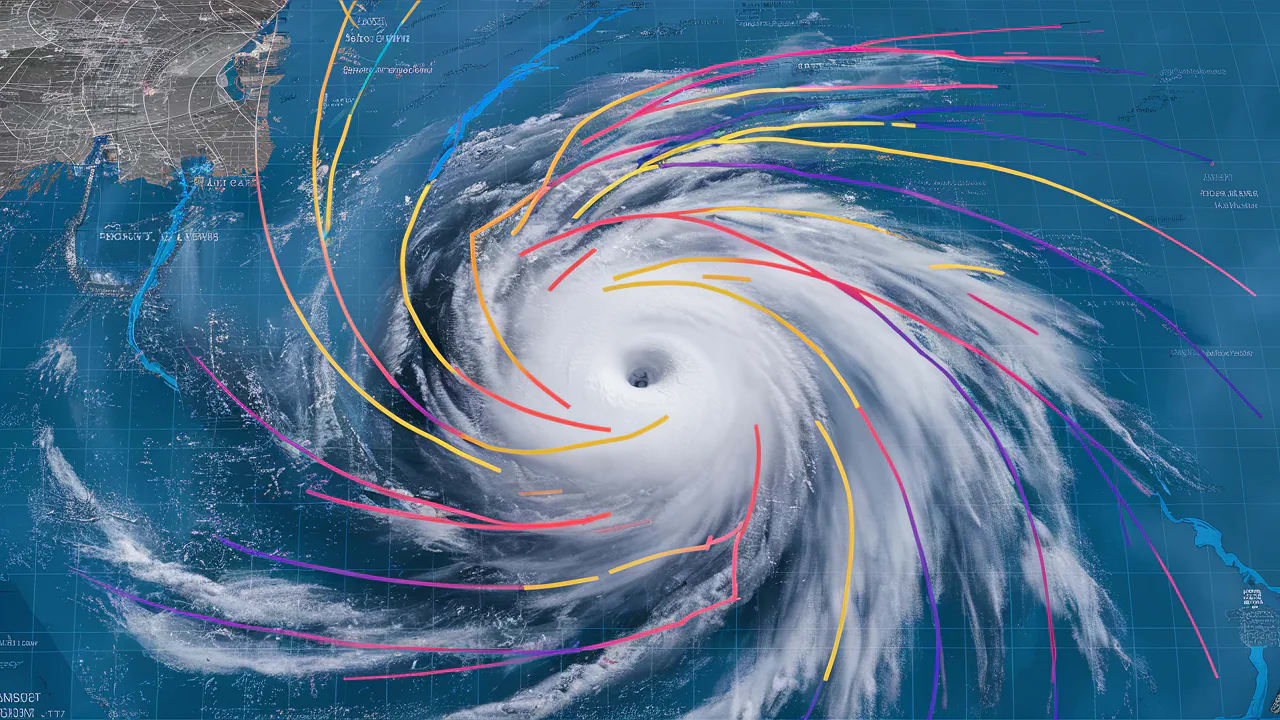 A comparison of forecast models used to predict jet stream behavior. This image shows how different models analyze pattern recognition, movement prediction, and trend analysis to forecast jet stream patterns.
A comparison of forecast models used to predict jet stream behavior. This image shows how different models analyze pattern recognition, movement prediction, and trend analysis to forecast jet stream patterns.
Forecast models are the workhorses of weather prediction. They use complex mathematical equations to simulate the atmosphere and predict future weather patterns, including jet stream behavior. These models take into account a variety of factors, including temperature, pressure, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation. a renowned Forecast Expert, explains: “Models predict pattern evolution.” While these models are constantly improving, they are not perfect. They are still subject to errors and uncertainties, particularly when predicting long-term weather patterns.
Model Types
Analysis Tools
- Pattern Recognition: Forecast models use pattern recognition algorithms to identify recurring jet stream patterns and predict their future behavior.
- Movement Prediction: These models also predict the movement of jet streams, taking into account factors such as temperature gradients and pressure systems.
- Forecasting tools: A variety of forecasting tools are available to help meteorologists predict jet stream behavior.
- Trend Analysis: Forecast models also analyze trends in jet stream behavior, looking for patterns that can help them predict future changes.
Prediction Methods
- Short-Term Tracking: Short-term tracking focuses on predicting jet stream behavior over the next few days, using current weather data and model simulations.
- Long-Range Outlook: Long-range outlooks attempt to predict jet stream behavior over the next few weeks or months, using statistical models and historical data.
- Pattern Assessment: Pattern assessment involves analyzing jet stream patterns to identify potential weather risks, such as droughts or floods.
- Impact Evaluation: Impact evaluation assesses the potential impact of jet stream changes on different regions and sectors, such as agriculture and energy.
Conditions Change Impact
Pattern Changes

Surroundings change is undoubtedly impacting jet stream patterns. As the planet warms, temperature gradients are changing, which is affecting the strength and position of jet streams. Some studies suggest that space change is causing jet streams to become more wavy and erratic, leading to more extreme weather events. Understanding these long-term shifts is essential for preparing for the impacts of habitat change.
Change Types
- Position: Jet stream position is shifting, with some studies suggesting that they are moving poleward.
- Strength: Jet stream strength is changing, with some studies suggesting that they are becoming weaker and more variable.
- Stability: Jet stream stability is decreasing, leading to more erratic and unpredictable behavior.
- Pattern: Jet stream patterns are evolving, with some studies suggesting that they are becoming more wavy and extreme.
System Response
 System adaptation patterns to surroundings change impacts on jet streams. This image shows how monitoring, assessment, and planning are essential for adapting to the changing behavior of jet streams.
System adaptation patterns to surroundings change impacts on jet streams. This image shows how monitoring, assessment, and planning are essential for adapting to the changing behavior of jet streams.
Adapting to the changing behavior of jet streams is a critical challenge. We need to improve our understanding of how sphere change is impacting jet stream patterns and develop strategies to mitigate the risks associated with these changes. This includes improving our weather forecasting capabilities, developing more resilient infrastructure, and implementing policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Setting Change (IPCC) has warned that changes in jet stream patterns could lead to more frequent and intense extreme weather events, including heat waves, droughts, floods, and storms.
Response Factors
Adaptation Needs
- Pattern Monitoring: Monitoring jet stream patterns is essential for understanding how conditions change is impacting their behavior.
- Impact Assessment: Assessing the potential impact of jet stream changes on different regions and sectors is crucial for developing effective adaptation strategies.
- Context tools: A variety of domain tools are available to help us monitor and assess the impacts of field change on jet streams.
- Response Planning: Developing response plans is essential for preparing for potential extreme weather events caused by jet stream changes.
Management Steps
- Pattern Tracking: Tracking jet stream patterns over time can help us identify trends and predict future changes.
- Change Analysis: Analyzing changes in jet stream behavior can help us understand the impacts of sphere change.
- Impact Preparation: Preparing for the potential impacts of jet stream changes can help us reduce the risks associated with extreme weather events.
- Response Development: Developing effective response strategies is essential for mitigating the impacts of setting change on jet streams.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if jet stream behavior is normal?
Consider these factors:
- Seasonal Patterns: Jet streams typically follow predictable seasonal patterns, shifting northward in the summer and southward in the winter. Deviations from these patterns could indicate unusual behavior.
- Position Changes: Monitor the position of the jet stream relative to its typical seasonal location. Significant shifts could indicate abnormal behavior.
- Strength Variations: Pay attention to the strength of the jet stream. Unusually strong or weak jet streams can have a significant impact on weather patterns.
- Weather Impact: Observe the impact of the jet stream on weather patterns. Unusual weather events, such as prolonged droughts or severe storms, could be a sign of abnormal jet stream behavior.
How does the jet stream influence my local weather?
The jet stream affects:
- Storm Tracks: The jet stream guides the movement of storms, determining where they will hit and how severe they will be.
- Temperature Patterns: The jet stream influences temperature patterns by transporting warm and cold air masses.
- Precipitation: The jet stream can affect precipitation patterns by creating areas of rising and sinking air, which can lead to rainfall or drought.
- Wind Conditions: The jet stream is a major source of wind, influencing wind speed and direction in different regions.
What future changes can I expect in jet stream behavior?
Watch for:
- Pattern Shifts: Conditions change is causing jet stream patterns to shift, leading to more unpredictable weather.
- Intensity Changes: The intensity of jet streams is also changing, with some studies suggesting that they are becoming weaker and more variable.
- Position Variations: The position of jet streams is varying, leading to more extreme weather events in different regions.
- Weather Effects: These changes in jet stream behavior are having a significant impact on weather patterns around the world, leading to more frequent and intense extreme weather events.
Is there a spiritual lesson we can learn from the jet stream?
Absolutely! Just as the jet stream is a powerful force shaping the weather, God is a powerful force shaping our lives. We may not always understand His plans, but we can trust that He is guiding us, just as the jet stream guides the weather. And like the weather, our lives have seasons. Sometimes we experience storms, and sometimes we bask in the sunshine. But through it all, God is with us, providing strength and guidance.
Additional Resources
Educational Materials
- Jet stream science
- Weather patterns
- Landscape effects
- Atmospheric dynamics
Technical Resources
- Research papers
- Weather data
- Analysis tools
- Forecast guides
Remember: Understanding jet streams is crucial for comprehending global weather patterns. It’s also a reminder of the intricate and powerful forces that shape our world. And for me, it reinforces my faith in a Creator who orchestrates it all.
_


